
A Carefree Holiday May Shoot Up your Sugar Levels
Holidays are meant to relax, but they may also be the reason to gain some unwanted weight. Deserts are omnipresent

Holidays are meant to relax, but they may also be the reason to gain some unwanted weight. Deserts are omnipresent
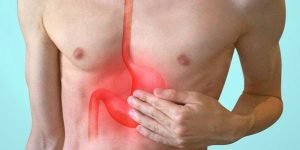
ACIDITY – AN OVERVIEW Acidity, a common digestive ailment, arises when the gastric glands in the stomach produce an excess
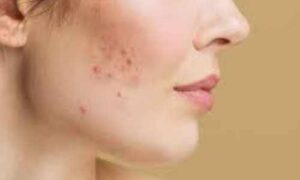
ACNE AND PIMPLES – AN OVERVIEW Acne and pimples, two dreaded words for anyone who has ever dealt with them. These
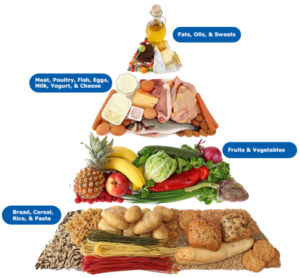
A Balanced Diet comprises of the following food groups. Carbohydrates : The bulk energy providers Proteins : The body building

That small bowl of ‘Halwa’ is awfully enticing, but there is something that holds you back, especially when you are

Making a blood sugar chart is a salient tool for diabetes. Charting Sugar Levels furnish functional information for diabetes administration.

What is Diabetes Diarrhea? A gastrointestinal obstacle of diabetes that perseveres from specific weeks to months called diabetes diarrhea. It

ARTHRITIS OVERVIEW Arthritis, a term that covers different joint problems, shows up as swelling, ache, and rigidity. This widespread ailment

By Dr Jyoti Monga For easy defecation our anal cavity has elastic tissue to help control the passing of excreta.

For easy defecation our anal cavity has elastic tissue to help control the passing of excreta. This tissue needs a
You're here>> Home
I’m looking for treatment / service for: